Efficacy of Implementation of 74th Constitutional Amendment
Act in Madhya Pradesh
Chapter-1 Introduction1.1 74th Constitutional Amendment
The Constitution (Seventy Fourth Amendment) Act, 1992 (74th CAA) which came into effect on I June 1993, introduced Part IX A (the Municipalities) in the Constitution. The Act provided a constitutional status to Urban Local Bodies (UL.Bs) in the country. Article 243W of the CAA authorized the State Legislatures to enact laws to endow local bodies with powers and authority as may be necessary to enable them to function as institutions of self-governance and make provisions for devolution of powers and responsibilities.
The Twelfth Schedule of the Constitution enumerates be devolved to ULBS.
1.2 Trend of urbanization in Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh, the central state of the country, is geographically the second largest State of the country. It covers almost 9.38 per cent of the area (308,252 Sq. Km.) and 6 per cent (727 crore), of country's total population. As per Census 2011, 2.01 crore (27.69 per cent) out of the total population resides in urban areas. The growth of urban population in the decade 2001-2011 was 41 lakh.
Urban Madhya Pradesh faces multiple challenges, namely, public health issues, poverty alleviation, waste management, depletion of natural resources, etc. In this scenario, ULBs have an important role to play, as most of these issues are handled best at the local level.
1.3 Profile of Urban Local Bodies
In Madhya Pradesh, three tiers of ULBS are categorized on the basis of population in their jurisdiction. There are 407 ULBs as shown in Table 1.1 below:
Table 11: Category-wise ULBs in Madhya Pradesh State
| Types of ULBS | No. of ULBS |
|---|---|
| Nagar Nigam (NN) | 16 |
| Nagar Palika Parishad(NPP) | 98 |
| Nagar Parishads (NP) | 298 |
| Total | 407 |
The Municipal Corporations (Nagar Nigam) are governed by Madhya Pradesh Municipal Corporations Act (MPMC) Act, 1956 and other ULB's viz Nagar Palika and Nagar Parishad's are governed by the Madhya Pradesh Municipalities Act (MPM) Act, 1961. Each Corporation/Municipal area has been divided into Wards, which are determined and notified by the State Government for the purpose of election of Councilors. All ULBs have an elected body comprising Mayor President as head of the ULB and Parshads/ Councilors as members of the Council.
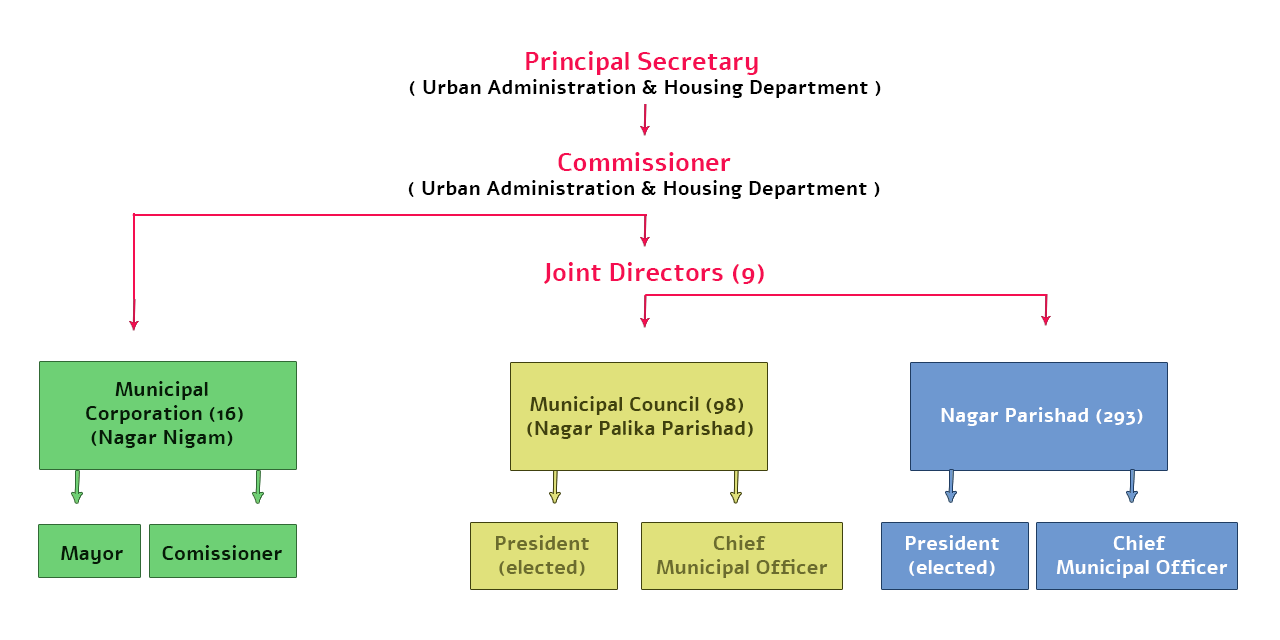
1.4 Organization Structure of Urban Governance in Madhya Pradesh
The Directorate, Urban Administration and Development (UADD) functions as an interface between the State Government and ULBs, which function directly under the Urban Development & Housing Department. Urban Administration and Development (UADD) is headed by Commissioner who is assisted by nine Joint Directors at Division level. The organization structure with respect to functioning of ULBs in the State is indicated in Appendix 1.
In addition to UADD, Urban Development & Housing Department has 10 key parastatal Agencies/ other Departments that deliver or facilitate urban infrastructure and services, such as the 28 Nagar and Gram Nivesh, Capital Project Administration (CPA) Bhopal, 19 State Institutes for Town Planning. 33 Divisions of Madhya Pradesh Housing and Infrastructure Development Board, Madhya Pradesh Rajya Karmchari Awas Nigam, Madhya Pradesh Public Works Department (PWD), Public Health Engineering Department (PHED), 50 District Urban Development Agency (DUDA), Madhya Pradesh Urban Development Company and Madhya Pradesh State Industrial Development Corporation (MPIDC). The details of parastatal and their functions are given in Appendix 2.
Organisational Chart of ULB
Appendix -2
List of Parastatals and their functions (Reference: Paragraph 1.4)
| Sr. No. | Parastatals | Functions |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nagar and Gram Nivesh | Formed in 1956 for preparation of development plans to establish the towns in organized and planned manners and to review such development plan at regular interval in terms of population of the town and prepare plan for State Development Plan. |
| 2. | Capital Project Administration (CPA) | After re-organizations of states, it was formed in 1956 for planned and rapid development of Bhopal, the newly formed capital of the Madhya Pradesh. The CPA Act to develop the different infrastructure/ basic amenity, to act as co- coordinator for various works and work according to requirement of capital region government buildings/ offices/ housing quarters and for beautification development of gardens, plantations, etc at large scale. |
| 3. | State Institute for Town Planning | Formed under Gram and Nagar Nivesh Act 1973. 10 Development Authorities- Bhopal, Indore, Gwalior, Jabalpur, Ujjain, Dewas, Katni, Singrauli and Anarkantak, Six Special Area Development Authoritis (SADA)- Panchmarhi, Gwalior Counter Magnet, Khajuraho, Orchha, Maheshwar, Mandleshwar and Chitrakoot; and three ULBS-Khajuraho, Dhanpuri and Grahakota are associate members of the institute. Primary objective of the institutes are: to assist and provide consultancy to Nagar and Gram Nivesh Department on subject matter on urban/ rural planning. |
| 4. | Madhya Pradesh. Housing and Infrastructure Development Board | Formed in 1972 as a corporate body under the Madhya Pradesh Griha Nirman Mandal Adhiniyam 1972. It was established to resolve the housing problems by way of development of land and constructing housing for various classes. |
| 5. | Madhya Pradesh Rajya Karmchari Awas Nigam | Formed in 1988 under Madhya Pradesh Society Registration Act, 1973 to resolve the housing problems of staff of State Government and Cooperative Societies established by Government. |
| 6. | Madhya Pradesh Public Works Department (PWD) | Public Works Department is the premier agency of Government of Madhya Pradesh engaged in Planning, Designing, Construction and Maintenance of Government assets like Roads, Bridges, Railway Over Bridges, Fly Over's and Buildings. The internal roads of the city which have not been handed over to the Municipal Corporation are being maintained by the PWD. |
| 7. | Public Health Engineering Department (PHED) | According to provision of the National Rural Drinking Water Programme, the Madhya Pradesh Public Health Engineering Department is responsible to provide safe and pure drinking water in the rural area of the state. The PHED is also responsible to prepare outline and co ordinate the activities of Water Augmentation Development Schemes of the entire state. The PHED is also responsible to operate the water qualities testing laboratories. |
| 8. | District Urban Development Authorities (DUDA) | At the District level, DUDA works as district level nodal agency for implementation of various livelihood schemes financed by the Central and State Government as well as provide assistance to people living below poverty line. |
| 9. | Madhya Pradesh Urban Development Company | Formed in January 2015 and responsible for preparation of Comprehensive Development Plan and execution of Externally aided Projects funded by World Bank, Asian Development Bank and KFW, one of the world's leading bank etc. for execution of sewerage and water supply schemes. |
| 10. | Madhya Pradesh State Industrial Development Corporation (MPIDC) | The MPIDC is responsible to develop land in industrial area and provide infrastructure facilities to the industries as single window. |